Wellington:
(04) 801 6228
Lower Hutt:
(04) 570 0520

Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the appliance's fit and effectiveness.
The dentist will also check for any changes in dental health or jaw alignment.
Alongside oral appliance therapy, dentists may recommend lifestyle changes like weight management, sleeping on the side instead of the back, avoiding alcohol before bedtime, and maintaining good oral hygiene.
Long-term monitoring is essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of the treatment and to make adjustments as needed.

Prevention and lifestyle changes can play a significant role in reducing or eliminating snoring. Here are some key strategies:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight, especially around the neck, can increase the likelihood of snoring by narrowing the airways. Losing weight can reduce snoring in overweight individuals.
2. Sleep Position: Sleeping on your back can cause the tongue and soft palate to collapse to the back of the throat, blocking the airway and causing snoring. Sleeping on your side can help prevent this.
3. Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax the muscles in your throat, increasing the risk of snoring. Avoiding alcohol and sedatives, especially close to bedtime, can help reduce snoring.
4. Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can help tone the muscles in your body, including those in your throat, which can reduce snoring.
5. Establish Good Sleep Hygiene: Regular sleep patterns and adequate sleep can reduce snoring. Create a comfortable sleep environment and stick to a consistent sleep schedule.
6. Manage Allergies: Allergies can block nasal passages, forcing you to breathe through your mouth and increasing the likelihood of snoring. Treating allergies with medication, nasal sprays, or allergy shots can help.
7. Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can lead to the formation of sticky mucus in the mouth and throat, which can increase snoring. Drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day can help.
8. Quit Smoking: Smoking irritates the membranes in the nose and throat, which can block the airways and cause snoring.
9. Raise the Head of Your Bed: Elevating the head of your bed by a few inches can help prevent the tongue and soft palate from collapsing into the back of the throat.
10. Nasal Strips or External Nasal Dilators: These can help keep the nasal passages open during sleep, reducing snoring in some people.
11. Use a Humidifier: Dry air can irritate respiratory membranes and contribute to snoring. A humidifier can add moisture to the air and reduce snoring.
12. Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Poor oral health can impact breathing and contribute to snoring. Regular brushing and flossing can help.
13. Throat Exercises: Certain exercises can strengthen the muscles in the throat, reducing snoring. These exercises typically involve pronouncing certain vowel sounds and curling the tongue in specific ways.
These lifestyle changes are not only helpful in reducing snoring but also contribute to overall health and well-being. If lifestyle modifications do not improve snoring, or if there are signs of sleep apnea (like excessive daytime sleepiness, choking or gasping during sleep), it is important to seek medical advice.
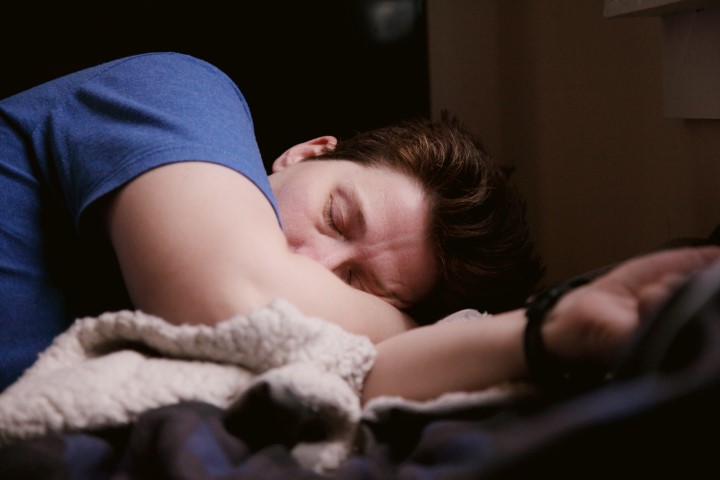
Snoring is a common condition that occurs when air cannot move freely through the nose and throat during sleep, causing the surrounding tissues to vibrate and produce the characteristic snoring sound. This is often due to relaxed throat tissues, and factors like pregnancy, weight
gain, sedative medications, and nasal congestion can contribute to snoring. To understand and manage snoring effectively, it's crucial to recognize its causes, risks, and explore potential solutions. For diagnosis, a doctor will review the individual's signs and symptoms, medical history, and may perform a physical examination. Information from a sleeping partner can also be invaluable in assessing the severity of snoring. For comprehensive information and in-depth guidance on snoring, the following resources can be very helpful:
1. Sleep Foundation's Guide on Snoring: This guide provides detailed information on the causes, dangers, and treatment options for snoring. It discusses various factors that contribute to snoring and offers up-to-date, fact-checked information. Snoring: The Causes, Dangers, & Treatment Options | Sleep Foundation
2. Doctor’s Comprehensive Guide to Stop Snoring: Authored by Philip Scolaro, MD, this guide provides insights from a medical perspective on how to stop chronic snoring. It is particularly useful for those who have been dealing with snoring for an extended period. How To Stop Snoring: A Doctor’s Comprehensive Guide
3. Mayo Clinic on Snoring: The Mayo Clinic offers professional guidance on diagnosing and treating snoring. This resource is valuable for understanding the medical approach to managing snoring. Snoring - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
4. HelpGuide's Remedies, Devices, and Cures: This source provides practical advice on remedies, devices, and cures for snoring, emphasizing lifestyle changes and home remedies. How to Stop Snoring: Remedies, Devices, and Cures
5. Comprehensive Guide by The Center For Sleep Apnea and TMJ: This guide offers an in-depth look at snoring, including its causes, risks, and potential solutions, curated by specialists. Understanding and Managing Snoring: A Comprehensive Guide
These resources provide a broad spectrum of information, from basic understanding to detailed medical advice, helping individuals to better understand and manage snoring effectively.
